aggra-guide
Hello World
This wiki presents an extremely simple version of the typical starting “Hello World” program as written in Aggra.
Let’s take a look at the data dependency diagram for this example first:
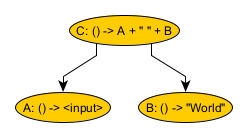
There are three nodes.
- Node A returns the input provided to the graph.
- Node B returns the string “World”.
- Node C calls nodes A and B and then joins them with a space separator. The result is the string “<input> World”. So, for an input of “Hello”, the result is “Hello World”
Now, here’s the code for creating and calling this graph:
public class HelloWorld {
// Every Graph needs a Memory subclass
private static class HelloWorldMemory extends Memory<String> {
private HelloWorldMemory(MemoryScope scope, CompletionStage<String> input) {
super(scope, input, Set.of(), () -> new ConcurrentHashMapStorage());
}
}
// Create the Graph and nodes (static is used for this example; Spring/Guice are just as valid)
private static final Node<HelloWorldMemory, String> GET_HELLO_WORLD;
private static final GraphCall.Factory<String, HelloWorldMemory> GRAPH_CALL_FACTORY;
static {
// Create the nodes in the graph
Node<HelloWorldMemory, String> getHello = Node.inputBuilder(HelloWorldMemory.class)
.role(Role.of("GetHello"))
.build();
Node<HelloWorldMemory, String> getWorld = FunctionNodes.synchronous(Role.of("GetWorld"), HelloWorldMemory.class)
.get(() -> "World");
GET_HELLO_WORLD = FunctionNodes.synchronous(Role.of("GetHelloWorld"), HelloWorldMemory.class)
.apply((hello, world) -> hello + " " + world, getHello, getWorld);
// Create the Graph and a convenient GraphCall factory
Graph<HelloWorldMemory> graph = Graph.fromRoots(Role.of("HelloWorldGraph"), Set.of(GET_HELLO_WORLD));
GRAPH_CALL_FACTORY = GraphCall.Factory.from(graph, HelloWorldMemory::new);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Observer observer = Observer.doNothing(); // We don't want to observe any node calls
GraphCall<HelloWorldMemory> graphCall = GRAPH_CALL_FACTORY.openCancellableCall("Hello", observer);
CompletableFuture<Reply<String>> helloWorldDoneOrAbandoned = graphCall
// Best practice is to set a timeout if calling join on unknown Future
.finalCallAndWeaklyCloseOrAbandonOnTimeout(GET_HELLO_WORLD, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
HelloWorld::handleCallState);
// Either the following throws (if abandoned and reply not done) or is fine (and helloWorld is fine)
Reply<String> helloWorld = helloWorldDoneOrAbandoned.join();
System.out.println(helloWorld.join());
}
private static void handleCallState(GraphCall.State state, Throwable throwable, Reply<String> finalReply) {
if (state.isAbandoned()) {
System.out.println(
"Error: we had to abandon graph call. Some processes may still be running in the background");
}
if (throwable == null) {
state.getUnhandledExceptions().stream().forEach(t -> t.printStackTrace());
} else {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Further wikis in the Aggra guide will explain concepts more in depth, but here are some call-outs:
- HelloWorldMemory – every graph needs at least one Memory subclass associated with it. This memory is used in this example to provide input and memoize results from nodes (although memoization doesn’t really come into play here).
- Input – there’s one overall input to this graph, which is set to “Hello”.
- FunctionNodes – all nodes in this example have quick-executing code, so they utilize FunctionNodes.synchronous.
- Timeout – it’s a best practice to set a timeout on any direct calls to join for CompletableFutures in an unknown state. That’s definitely overkill in this specific example, since we know all nodes will complete right away. However, we still set a timeout here to demonstrate the pattern.
- handleCallState – when the GraphCall is weakly closed (or abandoned… although that’s not going to happen in this case), we handle any unhandled exceptions by printing them out. As with the previous point, this is overkill in this specific example, since we know there won’t be any unhandled exceptions. This is just to demonstrate the pattern.